Computers have become one of the most essential parts of human life. At present, computers can be easily seen in almost every sector or field even where it is most unexpected. There can be several different reasons why computers are actually required. We can summarize the reasons for the requirement of computers in three words: efficiency, accuracy, and reliability.
Nowadays, computers are making jobs easier for people. Computers can be used in everything from entertainment to communication to navigation to research. That is why this era is called the era of IT (Information Technology). And now, one cannot imagine a world without computers.
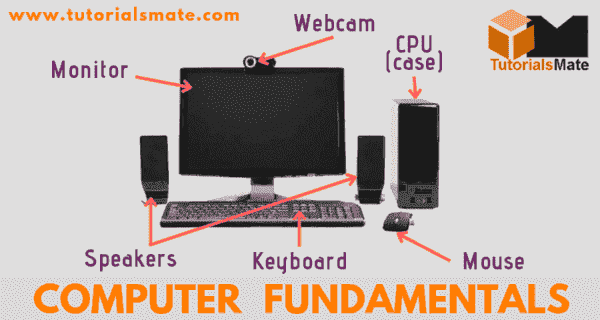
Therefore, it is very necessary to have knowledge of Computer basics. In this article, we have covered all the basics of the computer such as what is a computer, definition of computer, basic functions of a computer, generations of computer, classification or types of computer, advantages, and disadvantages of a computer, etc.
Prerequisites
There is no special requirement to learn the concepts of Computer fundamentals Tutorial. You just need to read the article properly. We have a well built and organized series of topics under Computer Fundamentals to help you in learning computer concepts from scratch.
Audience
Tutorials on TutorialsMate are designed to help beginners and professionals. Our Computer Fundamentals Tutorial will help beginners to master in Computer.
Problem
Our Computer Fundamentals Tutorial is designed by professionals, and we assure you that you will not find any kind of problem. In case there is any mistake, we request you to submit the problem using the contact form or directly send us a mail at TutorialsMate.
What You Will Learn
What is Computer
In 1640, the term ‘Computer’ was initially referred to as ‘one who calculates’. Later in 1897, it was called the ‘Calculating Machine’. In 1945, it was indicated as ‘programmable digital electronic computer’ which is now called a ‘computer’.
What is Computer definition?
“A computer is a programmable electronic machine designed to take input, perform prescribed arithmetic and logical operations at fast speeds, and provide the output of these operations.”
The term ‘COMPUTER’ is an acronym for ‘Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for Technological and Educational Research’.
The term ‘Computer’ is derived from the Latin word ‘computare’, which is defined as- “to calculate”, “to count” or ‘to sum up”, etc. In other words, “a computer is a device that performs computation”.
Note- The first mechanical computer was designed in 1837 by Charles Babbage. It was called 'Analytical Engine'. It was the first general-purpose computer. Charles Babbage is known as the father of the computer.
Also Check: Block Diagram of Computer
Basic Functions of Computer
There are four basic functions of the computer: Input, Processing, Output, and Storage.
Input
The data is entered into the computer with the help of input devices. Like other electronic devices, a computer takes data in raw form (binary form). The user can enter the data in several formats such as the collection of letters, numbers, images, etc. The input devices convert the data in the binary form so that the computer can read the data.
Some of the main input devices of computer systems are listed below:
• Keyboard• Mouse
• Joystick
• Scanner
• Trackball
• Lightpen
Read More: Input Devices of Computer
Processing
The processing is the core functionality of the computer system. It is the internal process where the data is processed according to the instructions given to the computer. The data is executed sequentially and sent for further processing.
The processing speed may vary in different computer systems as the speed mainly depends upon factors like which type of Motherboard, CPU (Central Processing Unit) or RAM (Random Access Memory) you are using.
Suggested Article: Why is my computer so slow?
Output
The output is the information provided by the computer after the entire processing. It is also known as the result that can be stored in the storage devices for further use. The output devices retrieve the processed data from the computer and convert the data into a human-readable form.
The widely used output devices of computer systems are listed below:
• Monitor• Printer
• Projector
• Speakers
Read More: Output Devices of Computer
Storage
Storage is a crucial part of the computer system. It is used to store data or instructions before and after processing.
Generally, storage is divided into the following types:
Primary Storage
Primary storage devices store the inputted data and immediate calculation results. The data stored in primary storage is temporary and will be lost if they are disconnected from the power source. Random Access Memory is an example of primary storage.
Secondary Storage
Secondary storage devices are used to store the data permanently for future use. The data stored in the secondary storage devices is secure even if there is no power supply. Hard Disk Drive is the widely used secondary storage.
Also Check: Types of Computer Memory
Generations of Computer
Each generation of computers is a major technological development in technology a computer is/was being based on. Initially, the term ‘generation of computer’ was used to distinguish between different hardware technologies. At present, the term concludes both the hardware and software. More precisely, the term ‘generation’ is the development that changes the way computers operate. There can be different changes like making the device smaller, cheaper, more smart or powerful, etc.
There are five generations of the computer, which are listed below with approximate period:
First Generation (1946 - 1959)
Based on- Electronic Valves (Vacuum Tubes).Example- ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, etc.
Second Generation (1959 – 1965)
Based on- Transistors.Example- IBM 1620, IBM 1400 and 7000 series, CDC 3600, etc.
Third Generation (1965 – 1971)
Based on- Integrated Circuits (ICs).Example- IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP, etc.
Fourth Generation (1971 – 1980)
Based on- Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) Circuits.Example- DEC 10, STAR 1000, CRAY-1 and CRAY-X-MP, etc.
Fifth Generation (1980 – Present)
Based on- Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Parallel Processing Hardware.Example- Desktop, Laptop, NoteBook, ChromeBook, and UltraBook, etc.
Read More: Generations of Computer
Uses of Computer
As we have discussed above, the computer is the need for the digital era. It is helping people to complete their tasks in hours that were before taking several days or months.
Here, we have explained the most important uses of the computer system:
• can store important data.• can communicate with people around the world.
• used for the educational system.
• used for office works like data entry, support, development, etc.
• used in banking, finance, and marketing.
• used in government sectors.
• used in sports.
• used for Press and publishing.
• used for entertainment.
Classification of Computer
According to usage and functionalities, computers can be classified as:
Analog Computer – The computers used to process analog data (continuously varying data) are called ‘Analog Computers’. Analog computers are the most complicated machines for computation and process control. Examples of continuous data are pressure, temperature, voltage, weight, and speed, etc.
Digital Computer – Digital computers are personal computers. These are the widely used computers. These are commonly used for processing the data with a number using digits by utilizing the binary number system. These computers are intended to perform arithmetic and logical operations at a very high rate.
Hybrid Computer – Hybrid computers are the combination of analog computers and digital computers. These are as fast as analog computers and include memory and precision as digital computers.

Types of Computer
Supercomputer – Supercomputers are large and require huge space for the installation. They are the fastest and most expensive computers compared to others. They are used for performing huge complex calculations.
Mainframe Computer – Mainframe Computers are smaller than supercomputers, still, they comparatively huge. These are not as fast as supercomputers. These are expensive as well as take huge space for the entire setup. Mainframe computers can store huge amounts of data and they are capable to handle large calculations. These computers are usually found in banks and educational sectors.
Microcomputer – Microcomputers are inexpensive and support multi-user platform. These types of computers are mostly used by small organizations. Microcomputers are slower compared to supercomputers and mainframe computers. Microcomputers are called Personal Computer (PC).
Mini Computer – Mini computers are cheaper and easy to carry. Notebook and Tablet are examples of minicomputers.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer
Just like a coin, a computer system also has two sides: Advantages and Disadvantages. While there are several disadvantages of a computer system, but, the advantages overcome them. Let's discuss both advantages and disadvantages of the computer system:
Advantages of Computer
The main advantages of the system are listed below:
• Amazing Speed• Accuracy
• Huge Storage
• Multitasking Support
• Data Security
• Automation
• Reduced Cost
Disadvantages of Computer
The main disadvantages of the computer system are listed below:
• Unemployment• Health Issues
• Cyber Crimes
• Virus and Hacking Attacks
• Improper Use
• Spread of False or Inappropriate Content
• Negative Impact on the Environment
In-depth Guide: Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer
Computer Software
Computer software is a group of programming instructions designed to instruct the computer to perform specific tasks. Typically, a computer system is useless without software.
There are two types of computer software, as mentioned below:
System Software
System software connect the user and the hardware of the computer to interact with each other. System software provide the basic functionalities required to operate the computer system. These type of software provide an environment or platform for the other software to work on. System software run in the background.
Example: Operating systems (e.g., Windows, Linux, Android, etc.), Device Drivers, Firmware, and Utility software.
Application Software
Application software are customized software designed for personal use. These type of software help users for performing basic tasks such as online research, setting an alarm, designing, or even playing games. The application software runs in the frontend and mostly used by the end-users. Therefore, these are also called ‘end-user programs’.
Example: Word Processors, Multimedia Software, Web Browsers, Graphics Software, Photoshop Software, etc.
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware are the physical components or parts that jointly form a computer system. There are different types of hardware. Depending on the structure of the computer system, hardware can be installed inside or outside of the computer physical body.
Components of the Computer Hardware
The basic components of the computer hardware are listed below:
• Monitor• Keyboard
• Mouse
• CPU (Central Processing Unit)
• Motherboard
• RAM (Random Access Memory)
• Hard Disk Drive
• Printer, etc

Take Test: Basic Computer Questions (MCQ)
Summary
The computer plays an important role in our day-to-day life and we cannot think of life without it. While there are some disadvantages of computers, however, the advantages of computers overcome those disadvantages. Therefore, it is very important to have at least basic knowledge of computers to complete in this era of technology.
Bonus
We have also attached a PDF file of this Computer Fundamentals Tutorial which will help you read this tutorial anywhere without the need of the internet. Get your free copy of "Computer Fundamentals PDF" file using the below link:




















Please share this...